Understanding Dyslexia?
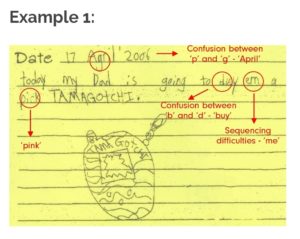
People often think that dyslexia is strictly the confusion of similarly written letters, such as b and d, but it encompasses much more. Dyslexia is a learning disorder that impacts one’s ability to not only read, but to speak, spell, and write. Specifically, people with dyslexia may have difficulty with decoding, or identifying speech sounds, and learning how they relate to letters and words. These difficulties typically result from a deficit in the phonological component of language. This, in turn, can lead to problems in reading comprehension and reduced reading experience that can impede the growth of vocabulary and background knowledge. These deficits have no impact on one’s overall intelligence, for those with dyslexia often tend to be very fast and creative thinkers. Typically, dyslexia is apparent in reading and language arts courses; however, students can struggle in any subject that contains any degree of reading. For example, they can have trouble reading and understanding math word problems. Dyslexia is considered to be the most common learning disability, affecting an estimated 17 percent of the population. Of those who have a learning disability, dyslexia is found in 80 to 90 percent of the cases. With prevalence rates this high, there is a very good chance that one of your students may be impacted by some degree of dyslexia.
Recognizing Dyslexia:
Preschool
- Delayed speech
- Slow acquisition of new words
- Difficulty with nursery rhymes or rhyming patterns
- Struggles with letter names and sounds
- Word formation problems (reversing sounds, confusing similar-sounding words)
Elementary School
- Difficulty comprehending spoken information
- Struggles with sequence recall
- Reading below grade level
- Challenges in sounding out words or pronouncing unfamiliar terms
- Trouble finding the right words or responses
- Difficulty discerning similarities and differences in sounds and words
- Spelling difficulties and inability to associate letters with respective sounds
- Slow reading or writing, delayed reading skill acquisition, or avoidance of reading-related activities
Ms. Eva Gogova